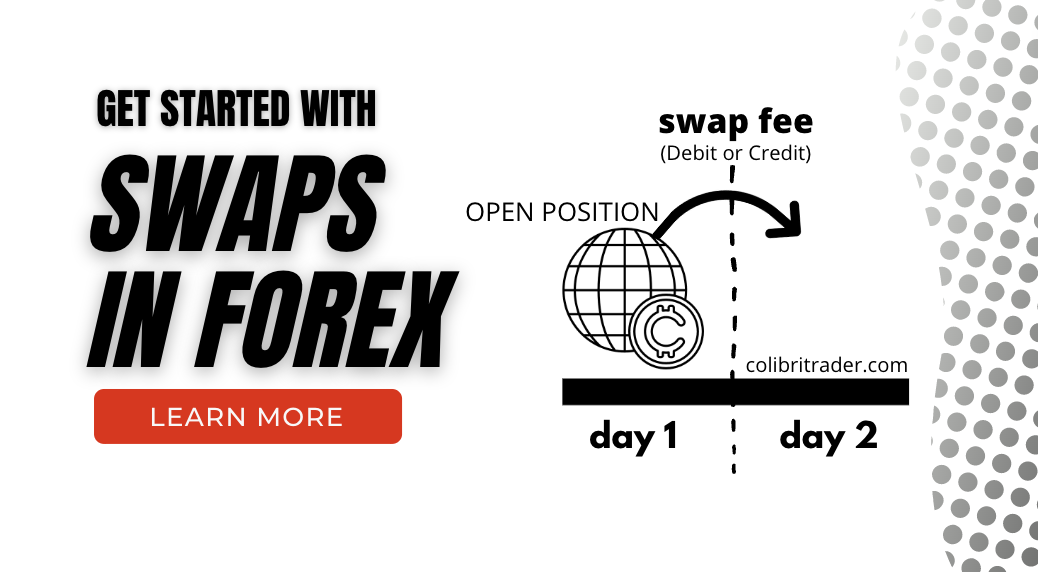
What Is Swap in Forex Trading?
You know, forex newcomers can get pretty overwhelmed trying to see what swaps are 🤓
Recall how you first got to know about the mechanics of forex trading.
It might be something like this:
“You buy and sell currencies with the lent money from a broker, requiring you to put out only a fraction of your own funds”?
Maybe you even thought you transact with other little fish traders like you?
This is only partially true, though.
The forex industry is slightly more complex than buying tomatoes from a neighbouring village and reselling them at a fair.
Hmm, is it really 🤔 ?
You can’t just buy $100k (standard lot) of base currency through your broker and keep it for an indefinite amount of time.
Especially if there’s only, say, $3000 in your account.
That’s when swaps and, of course, leverage come in handy.
The notion of swaps is integral in forex trading, especially for anybody holding trades for longer than a day.

Let’s figure out what swap in forex trading is and what role it plays in holding a position overnight.
Read on…
Contents in this article
What does swap mean in trading?
First of all, other than in forex, swaps are barely used in retail trading.
When two parties want to exchange cash flows to reach the risk exposure goals, they use swaps.
Here one needs fixed payments while another seeks variable ones.
On the institutional level, entities swap interest rates, commodities, currencies, debt, and even returns.
For instance, a hedge fund can bet on interest rate appreciation by getting a variable interest rate on a principal while giving up a fixed one.

Got it?
In Forex trading
Such an instrument helps us to swap currencies, not just once, but twice!
Why would one buy and sell or, conversely, sell and buy a certain volume of currency simultaneously?
We’ll get back to it, but first, let’s look at the terms of what we’re actually trading.

Got spot?
If a forex trader went short on EURUSD, they don’t directly sell the underlying euro but get a spot contract.
Aren’t we placing a foreign exchange trade “on the spot”?
In reality, a spot contract is a derivative that obligates the seller to deliver the underlying within two business days.
For certain currency pairs, it takes one business day.
In case of the long EURUSD position, would a trader deliver the USD?
Obviously, the retail forex trading industry doesn’t exist for mere exchanging currencies (there are banks and money changers for that!).

We open a forex brokerage account to speculate and make money!
Therefore, forex brokers would keep “extending” your spot contract using swaps until you close a position.
Drip, drip, drip money into your broker’s account…
Next, we’ll go into more detail on that.
How does swap in forex works
To extend the spot contract and avoid the delivery, brokers use tomorrow-next day (tom-next day) agreements.

Imagine you went long 0.5 lots of EURUSD at 1.0630.
You’d need to execute a swap trade to avoid the delivery and keep your trade for another day.
In this case, the swap involves selling your € 50,000 tomorrow and rebuying it using the new spot quote.
That’s why we literally “swap” it twice!
Let’s say now the price of your EURUSD position is 1.0645/1.0646.
To sell, we use 1.0645, and to buy – 1.0646.
But the new spot rate is higher: 1.06457/1.06472.
To hold the trade overnight, you’d need to sell at 1.0645 and buy again at 1.06472.
The rollover would cost you 2.2 pips.
The € 50,000 position equals around $5 per pip, translating into a 2.2*5=$11 fee, excluding a small administrative cost.
Got it?
The closing level of the position is adjusted with the interest rate.
In our example, we’ll be paid interest if the difference between ECB and FED interest rates is positive.

If the swap is negative, the interest will be charged.
How do you avoid the swap in forex?
If you don’t want to pay a swap fee, you can avoid overnight trading, negative rate differential, or classic forex accounts.
Let’s look closer at the three ways to avoid the swap in the list below.

1. Look for positive swap trades
Instead of being charged interest, you can earn one!
You can achieve this by buying a currency with a higher interest rate than the one you sell.
The classic example is going long AUDJPY: Australian dollar is considered the risk asset that usually offers a high-interest rate.
At the same time, the Bank of Japan traditionally keeps interest rates near zero to boost export.
2. Get out by forex session close
To avoid dealing with swaps, close all positions by 5 PM (EST) or your broker’s rollover time.
If you happen to trade intraday, it should be your normal practice.
3. Use an interest-free Islamic account
Many Muslim people want to trade forex, but according to Shariah law, one cannot take an interest in any deal.
Brokers found the solution to market their services to such a group of traders – swap-free accounts.
Usually, you’ll need to provide some proof that you’re a Muslim to open an Islamic account.
Still, you can find brokers that allow non-Muslims to use the swap-free account.
What is the swap cost in forex?
You may pay or receive the interest when you hold a position overnight in forex.
Of course, it will be viewed as a “cost” if you get charged.
So, what makes the cost to be a gain sometimes?
Let’s talk about some basics now👇🏽
Every currency you trade is issued by its respective central bank that sets a specific interest rate.
We trade pairs in forex, so when going long, you buy a base currency and sell a quote currency.
Conversely, the short trade is selling a base currency and buying a quote currency.
Imagine depositing the legal tender you buy and borrowing the one you sell.
You’ll be paid interest for the “deposit” and charged for your “loan.”
A working example
Let’s you want to buy one standard lot of USDCAD.
What kind of swap will you get if you hold the trade overnight?
As of writing, the US central bank – the Federal Reserve System, has a 1% interest rate.
At the same time, the borrowing rate of the Bank of Canada is 1.5%.
When buying USDCAD, we “deposit” the USD and receive 1% while paying 1.5% for the funding currency, the Canadian dollar.
Eventually, we’ll receive a negative swap of 1.0-1.5=-0.5%.
Imagine we hold this trade for a year, and the rates of both banks remain unchanged.
In this case, the swap cost will be roughly 100,000*0.005=500 Canadian dollars.
If you took the trade in the opposite direction (selling USD and buying CAD), you’d receive 500 CAD.
Not too bad, right 🙂
How is swap calculated in forex?
From the previous simplistic example, it may seem pretty straightforward how the swap is calculated.
However, we should also consider that on top of the interest rate differential, the broker’s fee, the markup is subtracted.
It almost sounded too good to be true, isn’t it.
At the end of the day, how are brokers supposed to make money if you’re a swing or a long-term trader?
Usually, guys who hold trades overnight use lower position volumes.
In addition, the trades aren’t frequent.
So, what kind of transaction fees can brokers expect?
Oh, poor them!
That’s why there’s a markup too.
Here’s the swap formula.
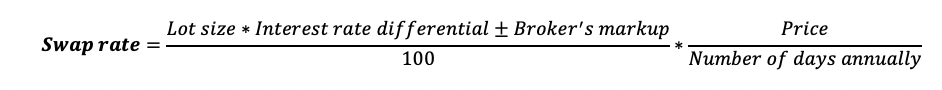
Notice, when calculating swap, we count interest inflow/outflow daily.
The “±” depends on the interest rate of the currency you’re buying or selling.
If the interest rate of the currency that you’re buying is higher, you subtract (“- “) the markup.
Conversely, in case of the higher rate of the funding currency (the one you sell), you add (“+”) the markup.
When are forex swaps charged?
Usually, brokers charge swaps at midnight of the local time where they are based.
For instance, suppose a trader is located in the US and holds a position through a London-based broker.
The swap charge would happen around 7 PM (GMT -4), as that’s when midnight is in the UK.
Often a common swap time is at the end of the New York session – at 5 PM (GMT-4).
Keep in mind that you would be charged a triple swap if you hold your position from Wednesday to Thursday.
You don’t see three days here, do you?
It takes two business days for banks to settle transactions in most currencies.
So, the trade you’re holding from Wednesday to Thursday (Wednesday midnight – the beginning of Thursday) will be settled on Monday.
The banks are closed on weekends, so Saturday and Sunday are skipped, and the trade is settled on Monday.
As a result, the swaps will also be applied to Saturday and Sunday.
A warning to seekers of the carry trades
A carry trade occurs when we buy a high-yielding currency against a low-yielding one, attempting to earn positive swaps.
For example, the Turkish lira currently has an interest rate of 14%, while the euro’s interest rate is 0%.
In theory, if we short EURTRY, we can expect to make 14% annually.
However, traders need to account for forex volatility risks.
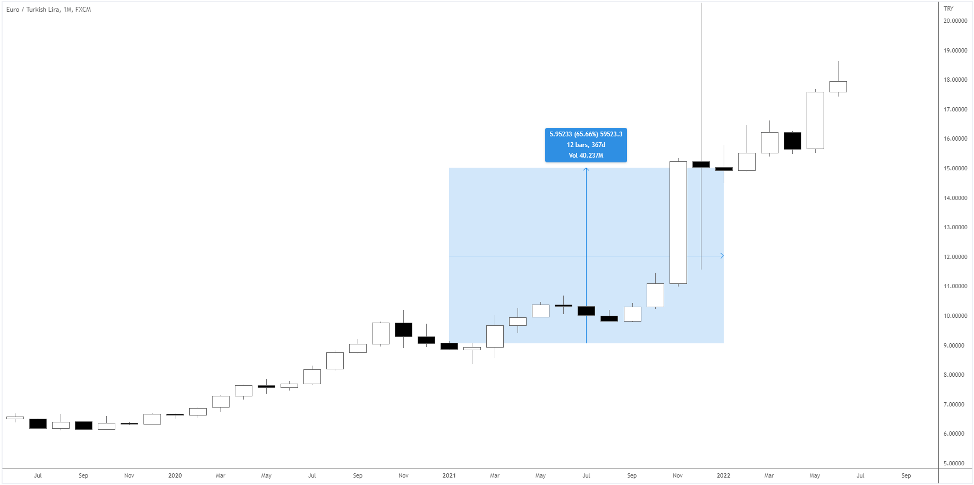
As you see above, the lira lost 65% against the euro in 2021.
Ouch!
Volatility risk is no joke, so make sure you consider it in your trade plan before entering the market.
Conclusion
A swap is a derivative that helps exchange cash flows – usually a fixed one for a variable one.
Forex swaps involve central bank interest rates, tom-next costs, and broker markup.
Depending on the interest rates differential, you’ll be charged or credited when you roll over a position.
The swap is applied around the end of the New York session, although it may depend on the broker’s server time.
You can trade intraday, open trades with a positive swap, or use an Islamic brokerage account to avoid negative swaps.
If you plan to open a trade to earn positive swaps, consider the forex volatility risks.
P.S.
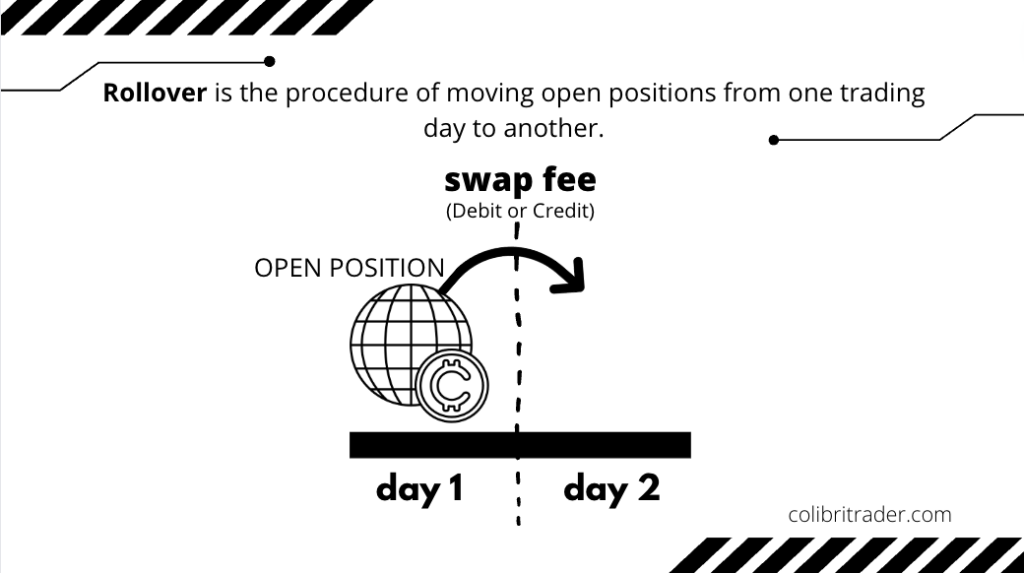
Here is rollover explained once again👇🏽
P.P.S.
If you don’t really care about Forex Swaps (but you really should), here is one very simple trading strategy that can help you overcome emotional trading (backed by hundreds of real traders’ testimonials)