Trading Hours for Futures
They say “money never sleeps,” and a futures contract is as close as it gets to measuring up!
A futures contract is famous for longer trading hours than the general stock market.
What are futures anyway?
The contract enables one to buy or sell an asset at an agreed price in the future while providing more flexible trading hours.
Are you struggling to follow the markets due to your personal schedule or time zone?
Futures can be the solution.
Depending on the asset, the trading hours vary.
Be sure that literally every second somewhere on the globe, the futures market is off and running, waiting for new orders!
Let’s dive deeper into futures trading hours below 👇🏽
Contents in this article
Do futures trade 24 hours?
On the CME, the futures on stock indices, metals, energy, currencies, interest rates, and cryptos trade for 23 hours.
It’s easy to remember these, as all follow the same schedule from 6 PM to 5 PM (ET).
So, what happens from 5 PM to 6 PM (ET)?
CME offers only one such instrument – MSCI Emerging Markets Index (ICE), trading from 8 PM to 6 PM (ET).
Are there any other futures to trade?
There are, on the another side of the globe!
Consider Australian futures; you can enter orders during the pre-market stage from 7 AM local time (5 PM ET).
Although, they won’t be executed immediately but put in a queue before they’re fulfilled three hours later!
Still, is there a way to actually execute a futures trade during this hour?
Digging deeper (earlier!), New Zealand’s Exchange (NZX) will let you place an index futures trade during the 9:00 AM-9:45 AM pre-open period (5-5:45 PM ET).
What time do S&P futures start trading?
There’s no big deal about the latter if you think of stock trading session opening vs. futures opening.
Why?
Index futures are derivatives that move according to the underlying stocks – the indices’ constituents.
If stocks aren’t traded now, it’s quite a guessing game what the “true” index futures contract price is.
Why would you risk it?
Thus, the futures volumes significantly decrease when the stock market is closed, including futures opening time.
Here’s an example.
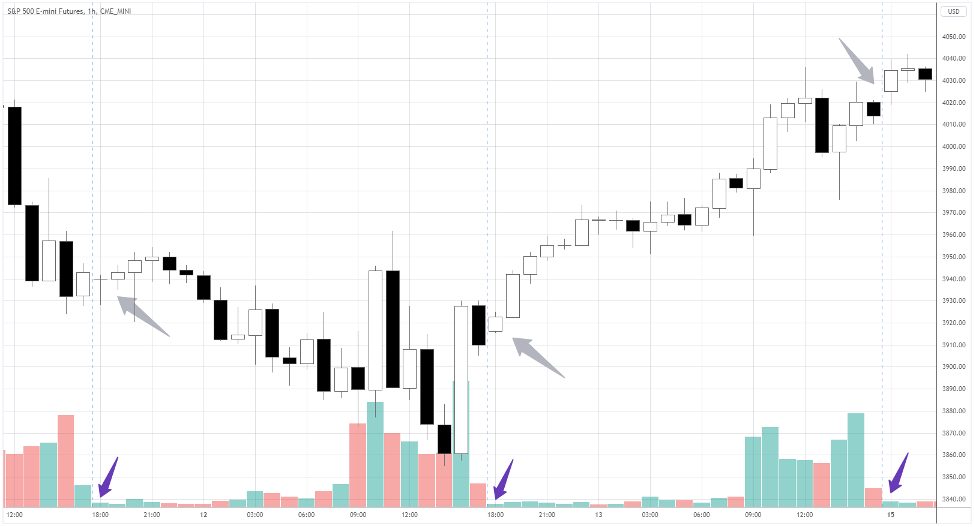
In the hourly S&P 500 chart above, the purple arrows point to the volumes (see the bars at the bottom) of the first hour of futures trading.
That’s a totally different story compared to the volumes within 8 hours before opening!
Grey arrows show little gaps between futures sessions’ closing and opening prices.
As the pause between sessions is only one hour, the gaps are usually small.
The most-traded markets worldwide are off, so there’s not much going on during that hour.
Do futures trade while the market is open?
This time is known as futures regular trading hours.
The rest of the time when futures are traded is electronic (extended) trading hours.
The stock exchange starts the main session at 9:30 AM (ET) and finishes at 4 PM (ET).
The post-market in stocks still lasts for an hour after the main session close, coinciding with the final hour in futures.
So, why does it matter?
The market is quite different during regular hours than extended ones.
Let’s look at the distinctions.
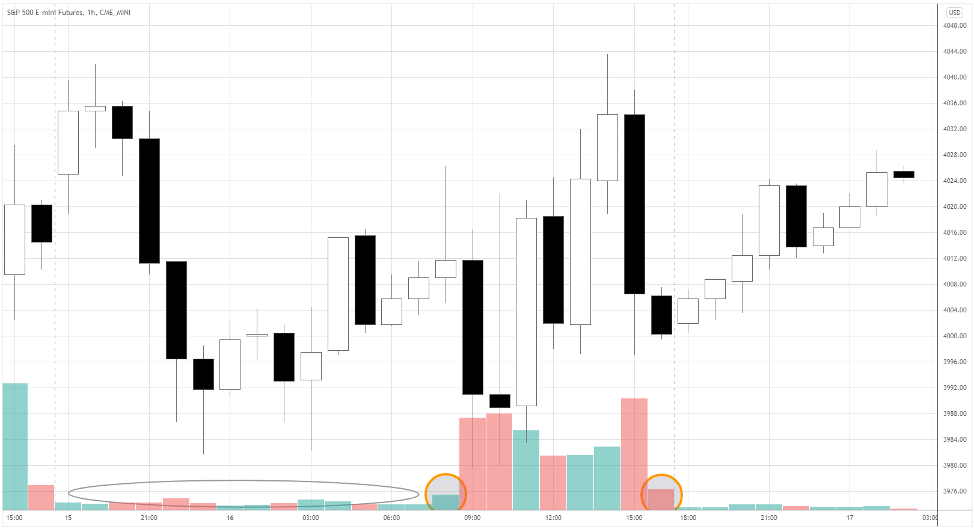
The ellipse in the chart above shows trading volumes during extended hours.
Compare it with the huge volume bars of the regular session.
Even the pre-and post-market volumes (see orange circles) are higher than the ones of electronic hours.
Notice the size of the candles that are formed by big volume – the volatility is much higher.
Also, each price swing is more reliable during regular hours, as weightier transactions form it.
You can be sure to hide your stop behind some fat limit orders!
Should I trade during extended hours?
We see those extended hours charts because some are willing to take additional risks and print in those limit players!
Why would they do that?
Let’s talk about it.
“In-play” market
When the market is driven by a non-standard event, like some breaking news, we call it “in-play.”
Short-term traders benefit immensely during such time, as the market is very directional, with many participants.
What if the market turns into the in-play one outside of the futures’ regular hours?
People would rush to react to the news in whatever market was available.
Suppose you were long S&P, holding the trade overnight, and something obviously bad happened during the electronic session.
You wouldn’t want to wait until the regular session opens, risking catching a gap in your face!
Of course, you’d be like, “get me out of here.”
When the Omicron variant was announced in South Africa on November 24th, people started selling futures during the electronic session.
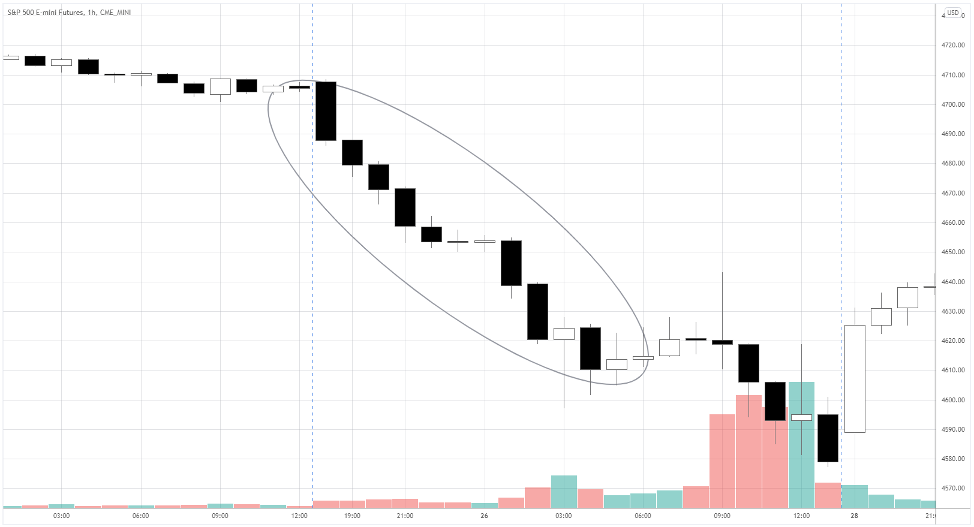
The chart in the ellipse shows the decline on the following day before the regular session opens.
Extended trading hours techniques
So, what are the specific tactics we can employ to trade the electronic session?
1. Watch alternative markets: Futures from different time zones tend to move in unison.
If you see a potential setup in, say, S&P, check what DAX is doing.
If the price action is similar, proceed with the S&P trade.
2. Wider stop and smaller size: Extended hours are more susceptible to noise.
Employ more conservative trade management, giving the market more room to breathe and betting smaller.
Summary
With a futures contract trading almost around the clock, traders can be more flexible in risk exposure.
Although the liquidity is very different during the electronic session, appropriate trading tactics should be used.
The quietest time in the world in terms of market activity is from 5 PM to 6 PM (ET).
As the sun rises in the eastern hemisphere, more futures markets open for trading.
Happy Trading,
Colibri Trader
P.S.
Did you read my article on the Best Momentum Indicators That Work?
P.P.S.
Have you ever wondered if SUCCESSFUL traders are born or made? Check out the Turtle Trading Strategy Rules here.