Trade Like Soros: Unlocking the Power of Reflexivity Theory for Market Success
George Soros is one of the most legendary investors of our time, building a multi-billion dollar fortune by exploiting market opportunities. Much of his success stems from understanding the psychological factors driving market behavior. His theory of reflexivity provides unique insights into these forces.
Contents in this article
Key Takeaways
- Reflexivity theory illustrates how market participants’ perceptions influence and shape economic realities, leading to self-reinforcing market trends.
- The theory explains market extremes and reversals, demonstrating how collective beliefs can drive prices to unsustainable levels before correcting.
- Reflexive trading strategies involve exploiting market biases by shorting overvalued assets, buying undervalued ones, and taking contrarian positions against herd behavior.
- Applying reflexivity theory in trading presents challenges like timing accuracy and personal biases, necessitating rigorous risk management and diverse portfolio strategies.
What is Reflexivity Theory?
Reflexivity theory states that market participant’s perceptions and expectations actually influence and shape economic fundamentals. There is a two-way, feedback loop relationship between perceptions and outcomes.
In essence, when enough people believe something is true in the markets, their actions can actually make it become true. The opposite also holds – expectations that are contradicted by the market can shift perceptions.

This self-reinforcing process creates booms and busts. Markets tend to push trends to extremes, as expectations alter realities until unsustainable, at which point the processes reverse.
Real-World Examples of Reflexivity
- Euphoric expectations for internet companies amplified the dot-com bubble in the late 1990s. This led to sky-high valuations until the market was severely corrected.
- The 2008 housing crisis was exacerbated by perceptions that real estate was a failsafe investment. Reflexivity took expectations too far, finally reversing in crashes.

Key Concepts of Reflexivity Theory
There are a few key mechanisms behind reflexivity in markets:
Misinterpretation and Distortion
People do not objectively process market information. Preconceptions alter interpretations of this data, leading to misjudgments. Confirmation bias exacerbates this effect.

Positive Feedback Loops
Initial market moves trigger reinforcing loops that foster further momentum. More price movement validates perceptions, drawing more participants and money flows.
Negative Feedback Loops
At extremes, reflexive processes reach points of unsustainability. Corrective, self-reinforcing forces emerge to reverse the trend.
The “Soros Reflexive” Trader
Skilled traders can identify market biases produced by reflexivity. By understanding a prevailing bias, they enter positions to anticipating the inevitable correction.
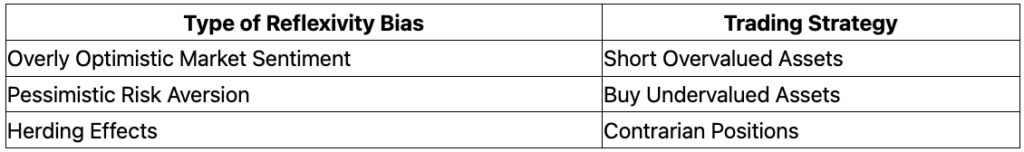
Practical Applications of Reflexivity Theory
Reflexivity theory offers useful models for trading success:
Identifying Market Bubbles
Warning signs of bubbles include:
- Rapid price acceleration over short periods
- Spikes in trading volumes
- Extreme valuations disconnected from fundementals
- Euphoric sentiment indicators
These suggest a prevailing bias vulnerable to reversal.
Shorting Overvalued Markets
By identifying overextended markets, traders can profit from coming corrections by shorting assets or buying inverse ETFs.
Managing Risk in Volatile Markets
Reflexive trading requires rigorous risk management. Set stop losses on positions, maintain balanced portfolio allocations, and avoid excessive leverage during periods of high volatility.
Potential Pitfalls of Reflexivity Theory
While potent, reflexivity theory has limitations:
Difficulty in Market Timing
It focuses on qualitative assessments of biases versus quantitative timing indicators, presenting challenges in perfect timing.
Behavioral Biases Among Traders
A trader’s own cognitive and emotional biases can distort how they perceive and act upon market reflexivity. Self-awareness is key.
Need for Portfolio Diversification
Reflexivity is best coupled with other analysis techniques and asset classes within a portfolio to mitigate risk.
Conclusion
George Soros’ theory of reflexivity provides a model for understanding and profiting from market psychology. By identifying prevailing biases, traders can position themselves for coming reversals. Combining these concepts with risk management best practices can yield substantial success.
For more on applying reflexivity theory in the markets, download our eBook Trading on Reflexivity or subscribe to our investor newsletter below!